Zone
A DNS zone is a portion of the DNS namespace that is managed by a specific organization or administrator.
Zone files and records
A zone file is a simple text file stored on a name server (NS) and provides information about one or more domain names. Each zone file contains a list of DNS records with mappings between domain names and IP addresses and other resources or their location.
Records
Within a zone file, records are kept. In its simplest form, a record is basically a single mapping between a resource and a name. They can:
- map a domain name to an IP address,
- define the name servers for the domain,
- define the mail servers for the domain, etc.
A Zone File with records inside:
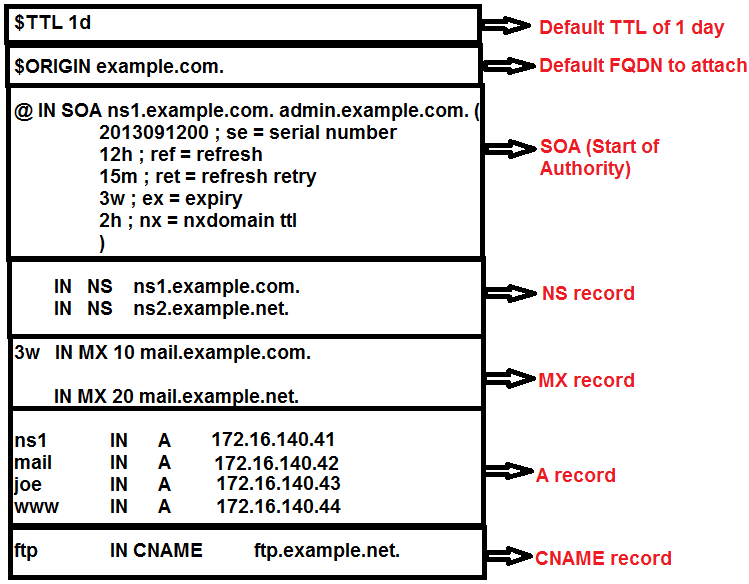
In short, zone file contains records which contains the mapping.
DNS uses a combination of record types to ultimately guide users to the right address for the Internet resource.
Zone file structure:

The field record class indicates the namespace of the record information. The most commonly used namespace is that of the Internet, indicated by parameter IN (stands for internet).
The field record type is an abbreviation for the type of information stored in the last field, record data.Ex: an address record (type A for IPv4, or type AAAA for IPv6 or a mail exchanger record (type MX).
The field record data may consist of one or more information elements, depending on the requirements of each record type.
Ex: an A record will contain IPv4 address.
Contents and records
TTL (Time To Live)
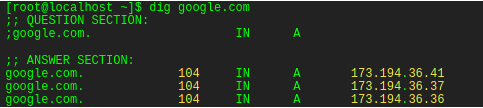
Dig (Domain Information Groper) is a network administration command-line tool for querying Domain Name System (DNS) name servers
The field ttl (time-to-live) specifies the time after which a domain name client must discard the record and perform a new resolution operation to obtain fresh information.
If ttl is not specified, the global TTL specified at the top of the zone file is used.
Above, the TTL value of 104 mentioned in the second column of the output is the number of seconds remaining for the TTL to expire.
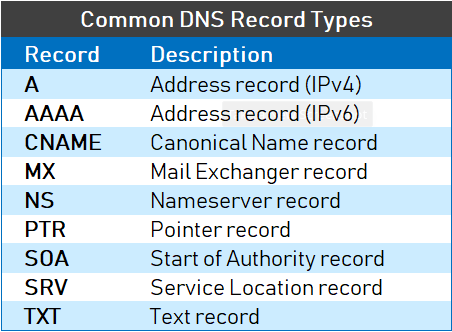
Resource Records (RR)
A single record that describes just one piece of information in the DNS database.
These records are simple text lines such as:
Owner TTL Class Type RDATA
Each of these field must be separated by at least one space.
- SOA Records
Start of Authority (SOA) is a mandatory record in all zone files. It specifies the main properties and characteristics of a zone (domain).
The SOA record for a zone contains data to control the zone transfer.
Format:
NAME TTL CLASS RR NAMESERVER EMAIL SERIALNUMBER REFRESH RETRY EXPIRY MIN
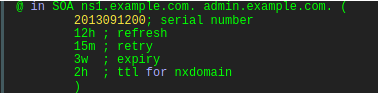
NAME: This specifies the name of the domain.
@ IN SOA ns1.example.com. admin.example.com.
@ = Name Vaule specified with $ORIGIN (example.com above)
$ORIGIN is used in the zone file to properly make all the records a FQDN record (ends with dot(.)).
Hence @ means example.com
TTL: Different records can have different TTL value.
CLASS: The default path used for all resource records are IN (Internet).
RR: This specifies the resource record name (SOA here)
NAMESERVER: The host name of the primary DNS server for the zone.
EMAIL: This specifies the administrative contact email address for this domain.
SERIALNUMBER: Serial number for this zone ,it tells the modification date of the zone file.
REFRESH: Indicates the time after which the secondary or slave DNS server for this domain re-fetches the SOA record for this zone.
RETRY: Specifies the retry interval if the slave will take, in case of a failure.
EXPIRY: This specifies the duration after which the slave name server will stop responding to DNS queries if the connection to master server cannot be established by following retry interval.
NXDOMAIN means non-existent domain name.
- NS (NameServer) Records
Identifies the authoritative DNS server for the zone.

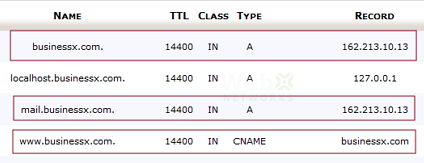
- A Records
The A (Address) record is used to map a domain or subdomain to an IPv4 address.
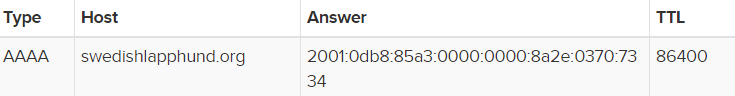
AAAA records point to an IPv6 record.
- CNAME (Canonical name) records
It maps one domain or subdomain to another domain name.

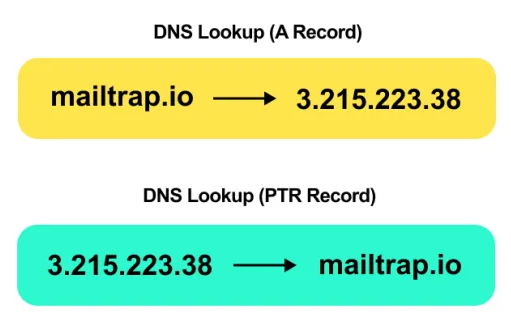
- Pointer records (PTR)
They are like the reverse of A or AAAA records.
It is used in reverse DNS records (i.e. from IP address to hostname).

- MX Records
It directs mail to a specific a mail server responsible for accepting of mail in the zone.

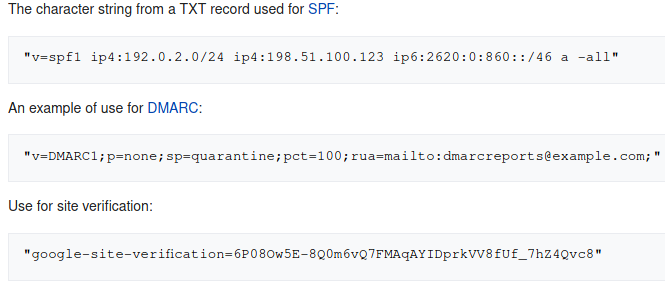
- TXT-Records (Descriptive text)
They are used to hold descriptive text.
They are often used to hold general information about a domain name such as who is hosting it, contact person, phone numbers, etc.
Dig or Nslookup command can be used to check different DNS records.